In Ireland, many organisations still rely heavily on paper-based records, which require physical management, movement, cataloguing, storage, and security. While document management systems and metadata tagging have been around for years, the adoption of digitisation solutions such as scanning for data capture and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for data extraction has been slower than anticipated. As we look to the future, the landscape of records and information management is set to undergo significant changes driven by digital advancements, AI, and evolving regulatory requirements.
Despite the availability of digital solutions, many organisations in Ireland continue to generate and manage paper-based records. This reliance on physical records presents challenges in terms of storage space, security, real-time accessibility, and long-term costs. However, the shift towards digital transformation is gaining momentum, driven by the need for more efficient and secure ways to manage information and the development of digitalisation capabilities and tools.
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES SHAPING THE FUTURE
Emerging technologies are revolutionising the way we manage and interact with information. From automating document classification to enhancing data security, these advancements are not only streamlining processes but also driving significant improvements in accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. This section delves into the transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on records management, highlighting key areas such as automated document tagging, AI-powered search engines, real-time security threat detection, and how these cutting-edge technologies are shaping the future of records management and paving the way for smarter, more efficient operations.
Automating Document Classification and Tagging
AI algorithms can automatically classify, and tag documents based on their content. This reduces the time and effort required for manual classification and ensures greater accuracy.
Streamlining Data Retrieval
AI-powered search engines can quickly locate and retrieve specific records from vast data repositories. These engines can also provide tailored suggestions based on user behaviour and previous searches, enhancing the overall search experience.
Enhancing Data Security
AI can detect and respond to security threats in real-time. By analysing patterns and anomalies, AI systems can identify potential breaches and take preventive measures to protect sensitive information.
Automating Records Retention Policies
AI can help organisations manage records retention by automatically applying retention policies based on the content and context of the documents. This helps to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and reduce the risk of retaining unnecessary records for longer than required.
Predictive Analytics
AI can analyse historical data to predict future trends and behaviours. In records management, predictive analytics can help organisations anticipate records management needs, optimise storage solutions, and improve decision-making processes regarding future needs.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables AI to understand and interpret human language. This technology can be used to analyse and summarise large volumes of text, making it easier to extract valuable insights from records. With NLP, users can also create workflows using natural language commands. For example, you can tell Power Automate to “notify the team when a new document is uploaded to SharePoint.”
Collaborative Records Management
AI can further support existing collaborative efforts by providing tools that allow authoring, automated workflows, intelligent search and insights, automated content management, and compliance. This can improve efficiency and ensure that all stakeholders have access to the most up-to-date information.
Cost Reduction through Automation
By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, AI can significantly reduce operational costs. This allows records management teams to focus on higher-level tasks and strategic initiatives.
THE ROLE OF GDPR AND DATA PROTECTION
Compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a critical aspect of records management. Organisations must ensure that as they pivot towards digital processes, personal data is handled securely and that records are maintained in accordance with GDPR requirements. This includes several key components:
Robust Access Controls
Access controls are essential to ensure that only authorised individuals have access to personal data, which involves identification and authentication, authorisation, monitoring, and auditing.
Accurate Records of Processing Activities
Maintaining accurate records of processing activities is a fundamental requirement under GDPR. Article 30 of the GDPR specifies that organisations must keep detailed records of their data processing activities, including: Data Controller and Data Protection Liaison/Officer contact details, purposes of processing, categories of data, data recipients, data transfers, retention periods, and security measures implemented.
Data Protection Measures
Organisations must implement comprehensive data protection measures to safeguard personal data. These measures include data encryption, data minimisation, data integrity and confidentiality, incident response planning, and third-party risk management, if applicable.
Employee Training and Awareness
Regular training and awareness programmes are crucial to ensure that employees understand their responsibilities under GDPR.
Realistic Expectations for the Future
While the vision of a completely paper-free office has not materialised as quickly as predicted, significant progress can be made in the near future. Organisations can realistically aim to:
- Increase Digital Adoption: Encourage the adoption of digital solutions such as scanning, OCR, and cloud storage to reduce reliance on physical records.
- Enhance Security: Implement advanced security measures, including AI-driven threat detection and blockchain technology, to protect sensitive information.
- Improve Accessibility: Utilise cloud-based solutions and IoT devices to ensure records are easily accessible and manageable from anywhere.
- Optimise Processes: Leverage AI and analytics to streamline records management processes, reduce manual tasks, and improve efficiency.
- Ensure Compliance: Stay up to date with regulatory requirements and implement best practices for data protection and records management.
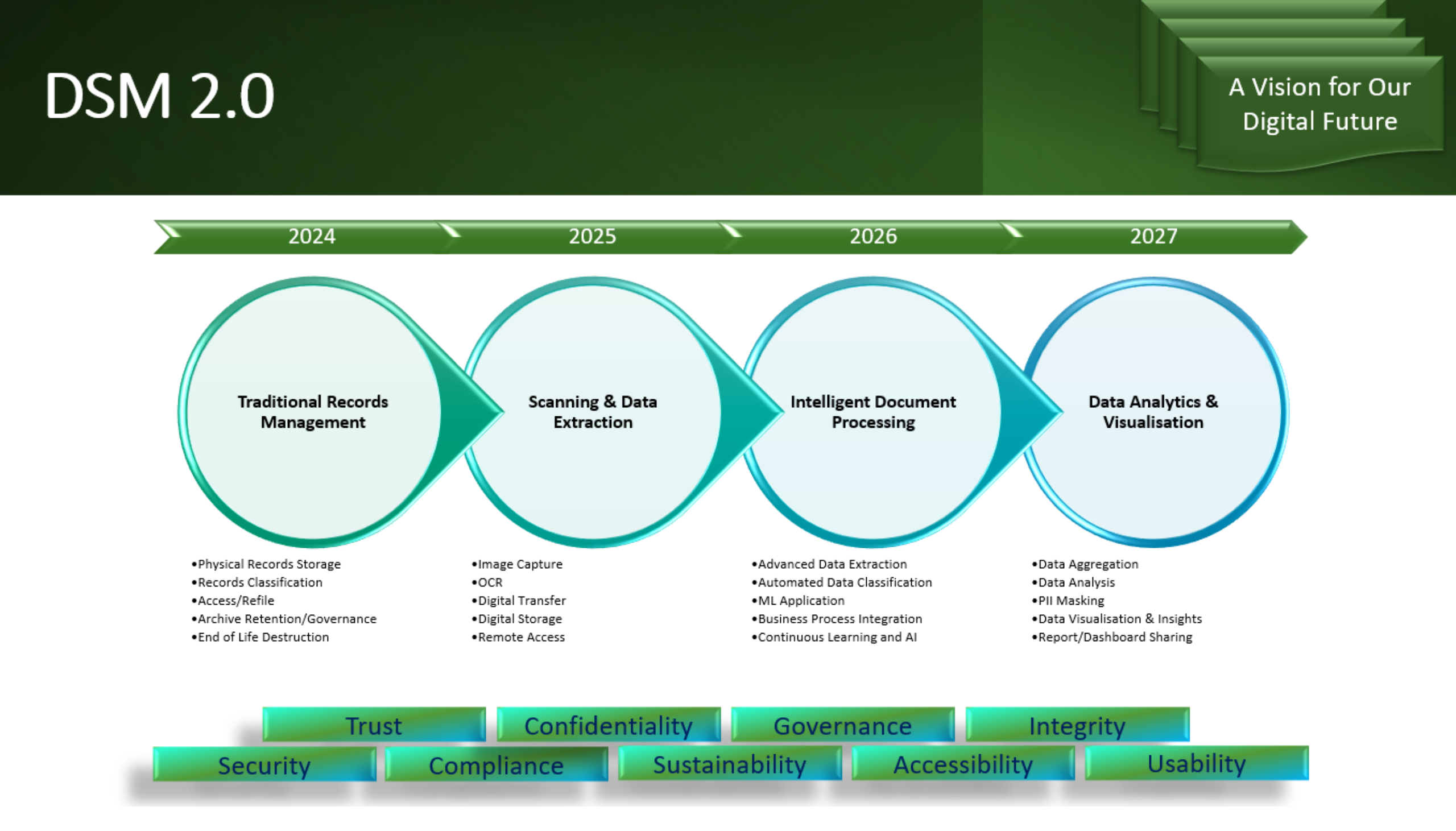
DSM FOCUS
While DSM has been focused on data storage, management, and security of physical records for many years, and will continue to do so for customers that require it, our focus has already shifted to providing digital solutions for our customers.
DSM is focused on building out comprehensive digital records management solutions for our customer base to include:
- Expansion of Digital Services: Continued investment in digital solutions such as advanced document scanning, OCR, cloud storage, intelligent document processing (IDP), and workflow automation. Integration with customer databases to enable seamless updates and ensure records are accurate and up to date, offering customers a comprehensive range of digital records management services.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Adoption of an advanced security infrastructure and environment protocols for perimeter defence, threat detection, and access control, including data masking techniques, to protect personally identifiable information (PII) and ensure compliance with GDPR.
- Intelligent Document Processing (IDP): Utilising AI-powered tools to enhance data security, automate processes, identify patterns and trends in data, predict future needs, and provide valuable insights to customers to support informed planning, decision-making, and improved operational efficiency.
- Customer Engagement: Engaging with our customers to provide training and resources to help them realise the longer-term benefits of digital transformation and encourage the adoption of digital records management solutions.
The future of records and information management is bright, with emerging technologies offering new opportunities for efficiency, security, collaboration, and compliance. While the transition to a fully digital environment may take time, organisations that begin to embrace these advancements will be well-positioned to thrive in the years to come.